Biomarker Development
A biomarker is generally defined as an indicator that can be objectively measured and evaluated to reflect a physiologic or pathologic process, as well as a biological effect of an exposure or therapeutic intervention. Biomarkers are primarily derived from human tissues or body fluids and can include alterations at the physiologic, biochemical, immunologic, cellular, and molecular levels. At the same time, there is a biological materiality as well as a measure of association with human physiopathology. Such measured changes are closely related to human physiological conditions, disease occurrence and development, and health status. It may include genetic variants, abnormal expression of protein receptors or changes in blood composition. Therefore, biomarker testing can be widely used in patient screening, diagnosis, clinical research, guidance of medication, prognosis, etc. The Technical Guidelines for the Application of Biomarkers in the Clinical Development of Antitumor Drugs issued by the CDE, and the BEST (Biomarkers, EndpointS, and other Tools ) by FDA and NIH can comprehensively and systematically guide the application of biomarkers in drug efficacy and safety studies.
Traditionally, clinicians use biomarkers to monitor therapeutic processes, disease progression, and intervention effects. According to the differences in functional characteristics of biomarkers, biomarkers related to drug development are usually categorized into the following six types: diagnostic, prognostic, predictive, effector, safety, and monitoring biomarkers. The same biomarker may have different functional attributes, and therefore the same biomarker may be categorized differently in different contexts of use.
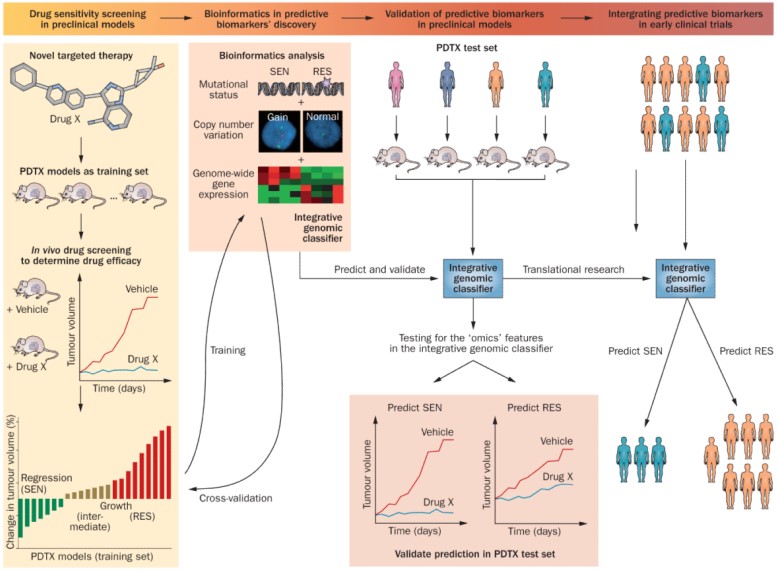
Tentler J, et al., Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2012;9(6):338-50
A mouse PDX model was used for biomarker discovery and validation
Pharmacodynamic test
Drug response in a PDX model;
Whole genome sequencing, transcriptome analysis, proteomics, metabolomics.
Analytical method development
Sequencing analysis of mutations, RT-PCR expression of genes, immunohistochemical expression of proteins;
Experimental verification
Select appropriate PDX models with positive and negative predictive biomarkers
Drug response of the selected PDX model