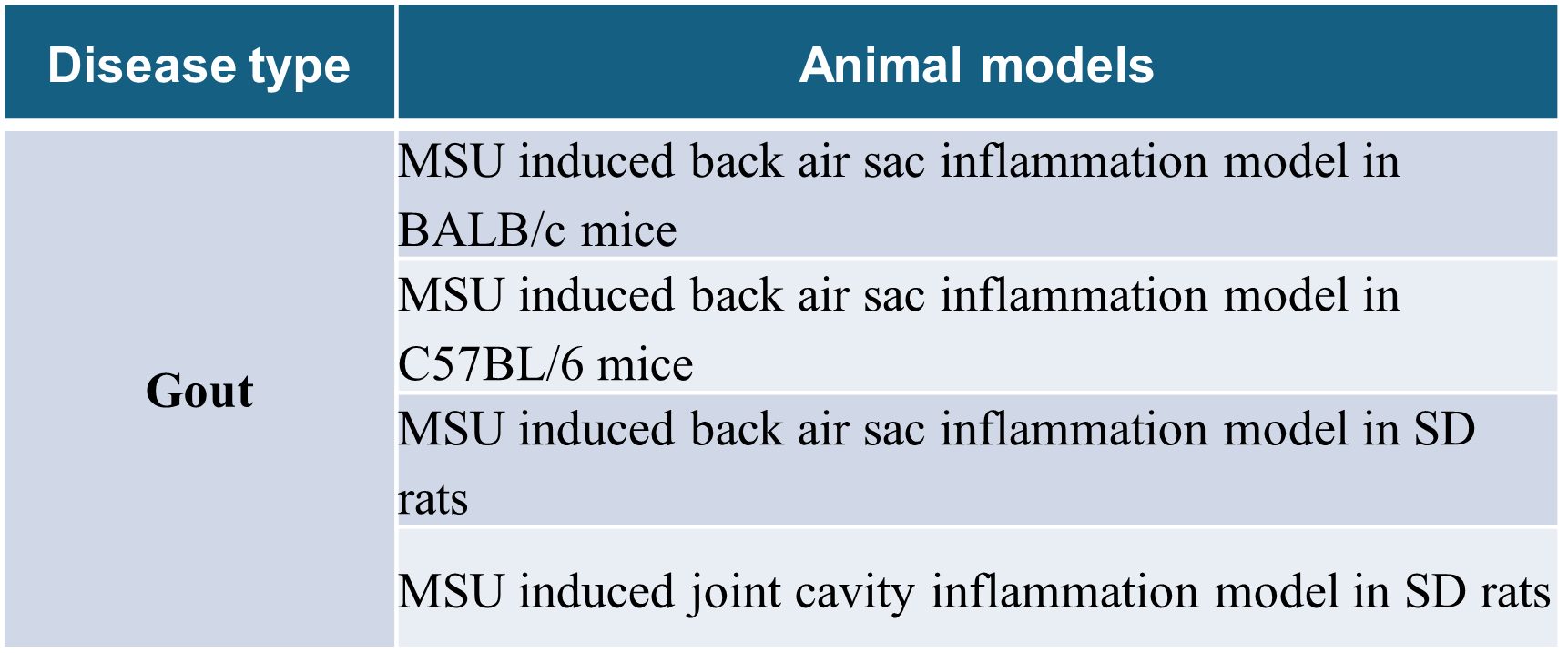
Gout
Gout, a disease caused by excessive deposition of uric acid, can occur in all age groups. High uric acid levels and deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals are the main causes of gout attacks.
Urate crystal formation is central to the pathogenesis of gout. When serum uric acid levels exceed their physical solubility (approximately 7 mg/dL), they precipitate as MSU crystals.
The precipitated MSU crystals are deposited in cartilage, synovium and surrounding tissues, and MSU crystals have leukocyte chemotactic properties and can stimulate leukocytes to release arachidonic acid, which can be oxidized by cyclooxygenase to generate inflammatory substances, causing non-specific inflammatory reactions, with the clinical manifestations of redness, swelling and heat pain in the joints and the surrounding soft tissues.

Lee JH, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022; 13:861399.
Gout animal models