Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is an autoimmune disease mediated by specifically sensitized CD4+ T cells and characterized by the presence of MC infiltration around small blood vessels and myelin sheath loss within the CNS, and its pathological changes are similar to those of MS.
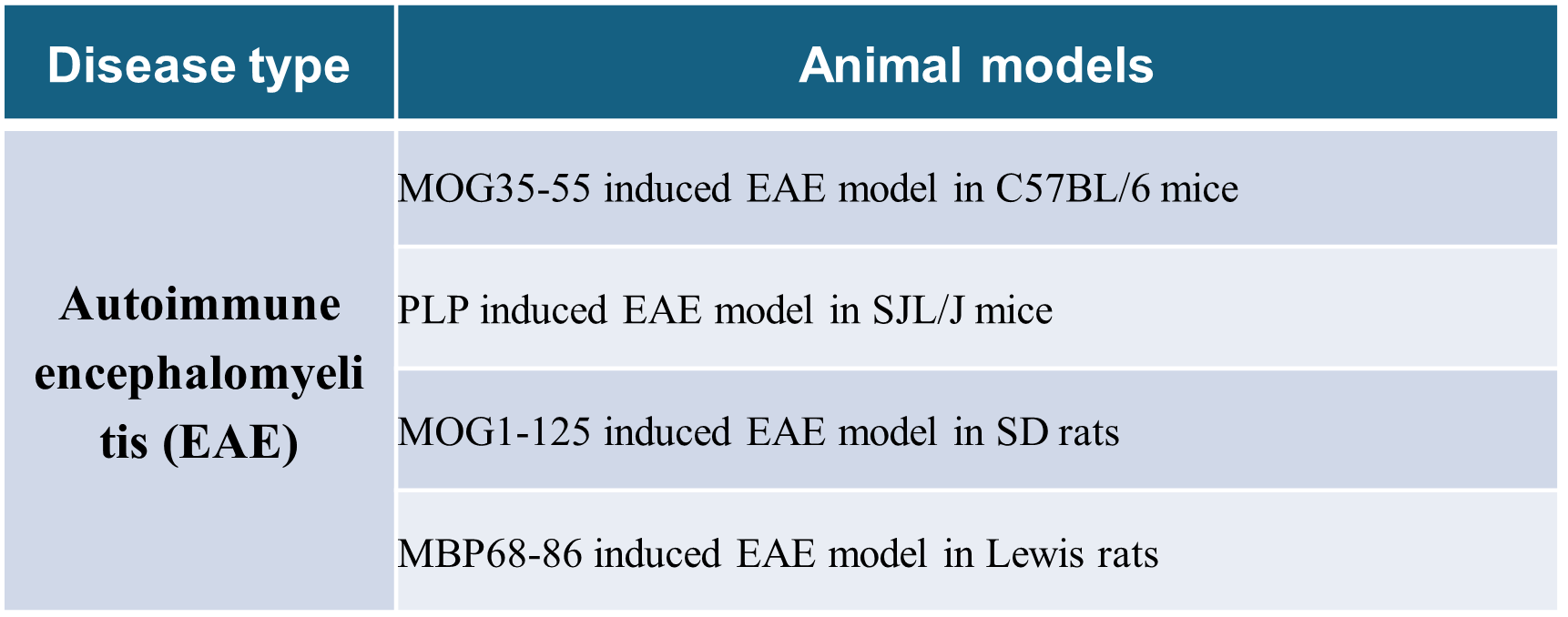
Commonly used sensitizing antigens:Myeloid oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG),Myelin basic protein (MBP);Protein lipid (PLP), etc.
A clinical classification of 5 levels of neurological function based on behavioral manifestations is usually used to judge the degree of morbidity.
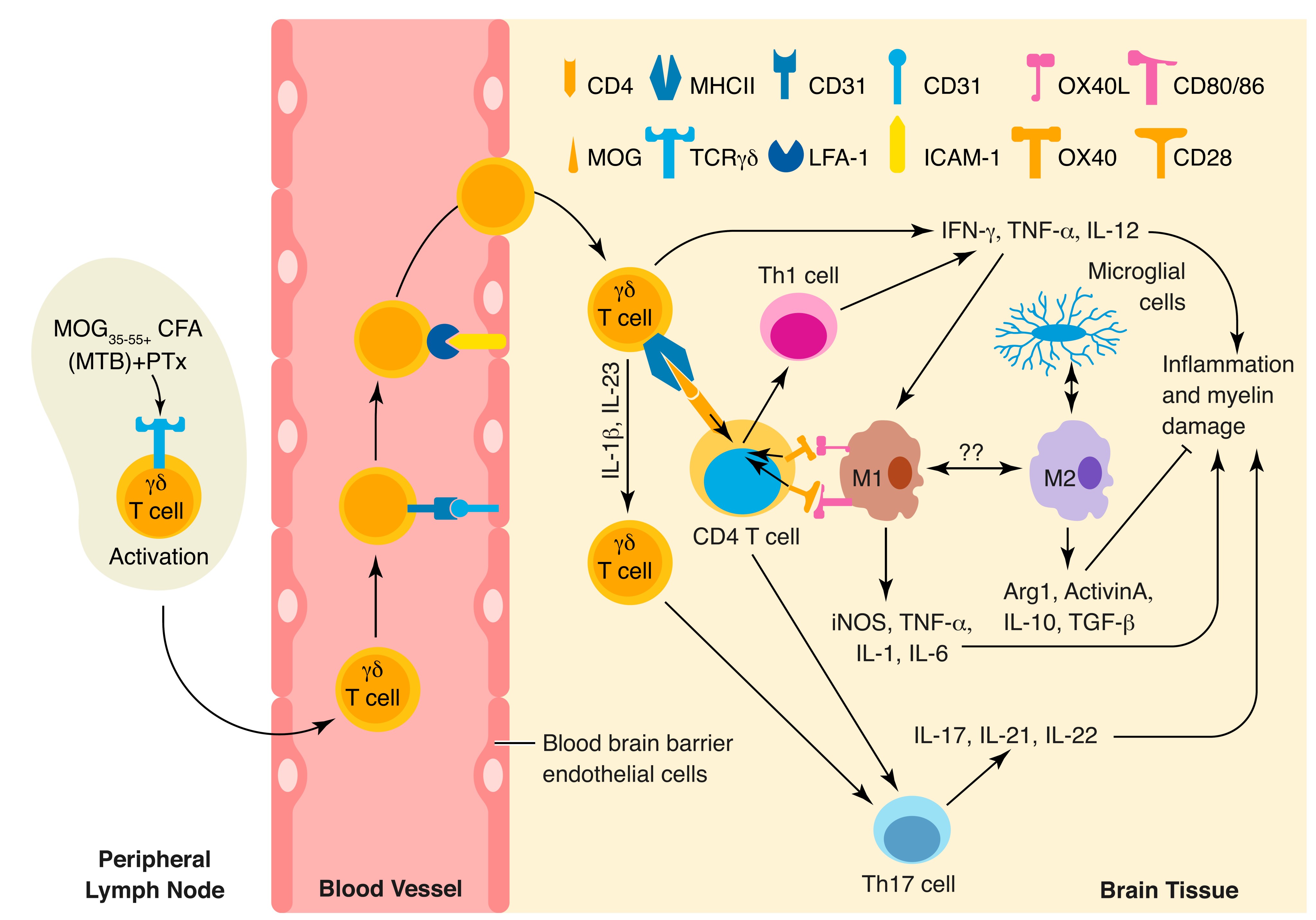
Paul S, et al., J Leukoc Biol. 2015; 97(2):259-71.
Animal EAE models