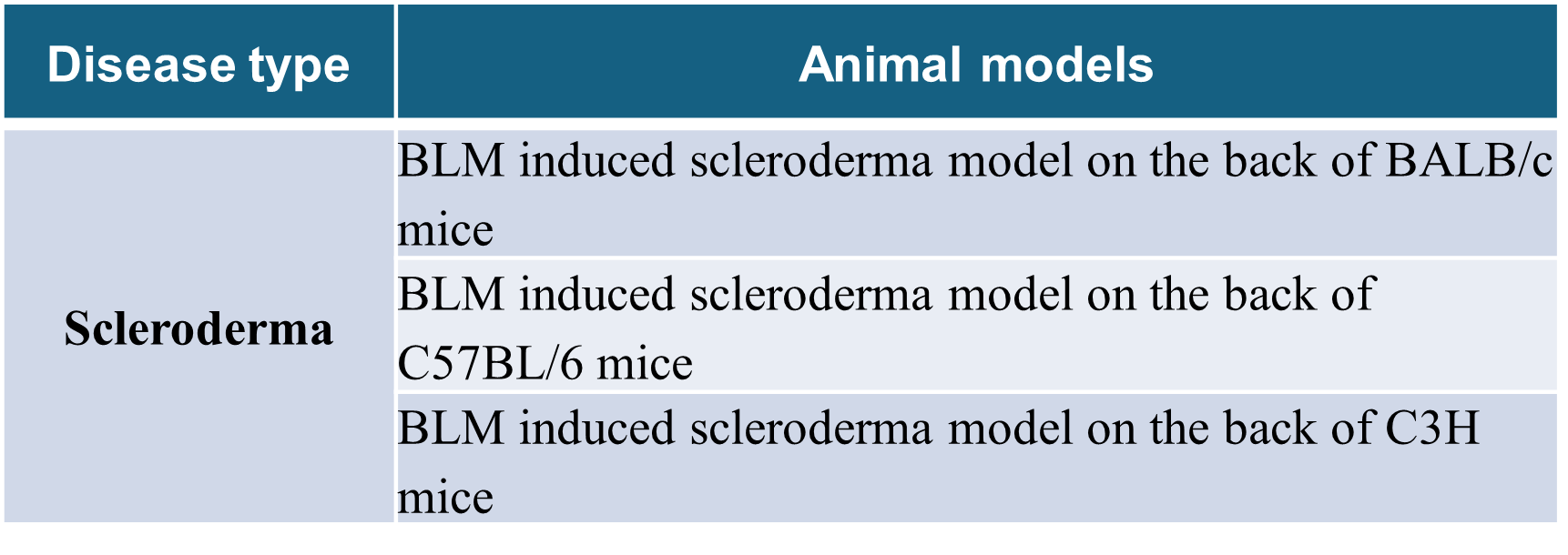
Scleroderma
Scleroderma is an autoimmune disease characterized by skin inflammation, degeneration, thickening and fibrosis, followed by hardening and atrophy, which can cause damage to multiple systems. The systemic sclerosis not only involves degenerative changes in the skin, synovium, and arteries of fingers (toes), but also can affect internal organs such as the digestive tract, lung, heart, and kidney.
The cause of the disease remains unclear. It may be due to the influence of genetic and environmental factors (viral infections, chemical substances such as silicon, etc.), female hormones, abnormal cellular and humoral immunity, the fibroblasts increase the synthesis and secretion of collagen, leading to fibrosis of the skin and internal organs.
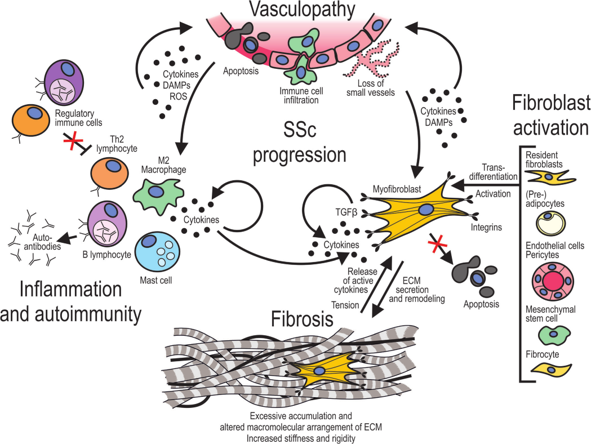
Rosendahl AH, et al. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2022; 38(3): 187-195.
Scleroderma animal model